A Streamlined Methodology for
Efficiently Managing Engineering Projects
Dr. Amartya Kumar Bhattacharya
Synopsis
 |
In developing countries like India engineering projects particularly those relating to the development of industry and infrastructure form a highlight area in the national economy. It is observed that many of these projects do not deliver the desired end result and eventually end up with substantial cost and time overruns. In depth analysis reveals that there are numerous and diversified causes for such failure of the projects. It is not wise to suggest a sure solution to this problem. Based on the experience of the authors on implementation of engineering projects in India and other developing countries a streamlined approach is suggested in this paper to achieve success in management of engineering projects. |
Introduction
A project signifies a scheme, a plan or a course of action. Managing a project means to handle, to conduct, to regulate, to organize and to control the project. So, project management is the art or science of conceiving, organizing, executing and keeping control on the project.
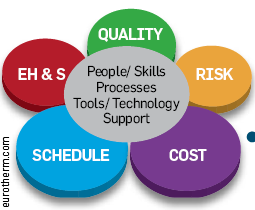
An engineering project is a collection of activities linked together to achieve the desired result, has a well defined purpose focused on the interest and expectation of the end users and must be completed conforming to the specified Quality, Time and Cost constraints. Such projects are normally complex due to the involvement of people of different disciplines in various departments and locations and have to be flexible enough to accommodate changes as the work proceeds. It involves risk at various stages and the management must coordinate and control the whole effort focusing attention on the desired end objective.
The term project is a very broad and general one and covers a wide spectrum of activities from a low cost rural housing project to a multibillion dollar missile or space project. This paper highlights construction projects of various magnitude and complexity with particular reference to Industrial and Infrastructure Projects that are ongoing at present or are in conceptual stage in India.
Management Strategy
Management’s main role is to Lead, Plan, Organize, Coordinate and Control the project ensuring optimum utilization of available resources, the four Ms that is, Manpower, Materials, Machineries and Money. In most Engineering Projects managing the first M namely, Manpower has been proved to be the most complex and crucial one.
Management Strategy is an essential first step in execution of an Engineering Project. Many projects fail due to the strategy not being formulated at the outset and not followed through. Hence, it is imperative that the strategy for managing the engineering project must be formulated and laid down during the conceptual planning of the project.
Project Life Cycle
The life cycle of a project broadly consists of four distinct phases that normally overlap with each other in a real life project. The phases are as follows:
Phase 1 - Project Concept consisting of
- Conducting location survey and site selection
- Conducting alternative studies on the project
- Fixing project goals
- Establishing overall project criteria
- Outlining possible strategies
- Making preliminary plans with costing and scheduling.
Phase 2 - Project Development consisting of
- Plan resource utilization, the four M’s namely, Manpower, Materials, Machineries (Equipment) and Money (Cost).
- Detailed plans namely, Project Scope, Project Completion Time (Schedule), Project completion Cost (Cash flow) and Project Quality (Quality Assurance and Quality Control or QA/ QC).
Phase 3 - Project Implementation consisting of
- Project Organization
- Communication within and outside the project organization
- Project Implementation Plan and Monitoring progress on the project
- Adjust the initial plan to suit changed situation and continuous follow-up
- Motivate and Lead the project team members and agencies involved to achieve best result
- Identify, Analyze and Solve problems in the course of project implementation.
Phase 4 - Project Termination consisting of
- Finishing the works
- Handing over operations
- Settlement of Disputes and Claims
- Overall Project Evaluation and Review
- Contract Closure
- Finalization of Project Records (FPR - Final Project Report or Project Completion Report) for future reference.
Project Milestones
A well managed project should have the following distinct milestones:
- Project Initiation
- Project GO AHEAD Decision
- Placement of Order (PO) for major contracts
- Construction and Installation substantially complete
- Project Handing Over for full occupation/ operation/ use.
Project Implementation Stages
The main stages in project implementation are as follows:
- Preparation of Detailed Project Report (DPR)
- Selection of process / methods and finalization of contracts
- Selection of Consulting Engineers and award of Consultancy Contracts:
- DDC - Detailed Design Consultancy
- DSC - Design Supervision Consultancy
- PMCC - Project Management Consultancy Contract
- Preparation and approval of Schedule, Cost Estimate and Budget
- Finalize Project Works Contracts
- Set up Project Organization
- Procure Equipment and Materials
- Project Construction:
- Land Acquisition and Site Survey
- Site Preparation
- Construction and Erection of Works
- Installation of Equipment and Service facilities
- Tests, Trial Runs, Start-up and Commissioning
- Management Reports for Progress Monitoring and Project Control.
Well Managed Project
A successful project may be defined as the one that has been completed conforming to approved quality standards within the stipulated time frame that is, on schedule, without any time overrun and within the approved budget i.e. without any cost overrun.
The essential factors in a well-managed project are an Efficient Project Team, Good Team Motivation, Good Leadership and Well-defined Project Objectives.
Management shortcomings are frequently noticed on Communication including Language bar, Establishing Priorities, Follow-up and Control and attention to the project related Human Aspects. Many projects fail due to Inadequate Strategy and Control, Lack of Leadership Commitment, Ill-Defined Goals, Delayed Decision, Ineffective Planning and Resource Mobilization, Political and Legal Obstacles.
Project Formulation
The project formulation normally includes the following major sets of activities:
- Investigation and Data Collection
- Assembly and Collation of data for planning
- Planning involving the following:
- Assessment of needs
- Identification of an appropriate approach to satisfy the needs
- Possible alternative measures and fixing priorities
- Decision on single or combination of alternatives
Inter-Departmental coordination is of utmost importance during the planning and implementation stages. Project formulation and its implementation are inter-dependent, so the implementation technique to be adopted should be clearly spelt out at the formulation stage. It should also be clearly assessed that the project would be sustainable on a long- term basis so that the desired benefits could be derived throughout the normal expected project life cycle.
Engineering Organization
Engineering Management is a team game where each player has to be carefully selected and each one plays his part efficiently in a well-coordinated manner. The aim is to put the right man on the right job. The organization should be kept flexible enough to meet the changes in situation during the life of the project. The higher management should select and appoint the Project Manager first. As the Team Leader it would be the prerogative of the Project Manager to select his team members. Once the basic organization structure has been finalized each position should be identified and job description prepared for each to ensure that all work is covered and there is no duplication of responsibility. The job description for each position should clearly define the following:
- What is the scope of job in that position?
- Who is the immediate supervisor?
- Who are the subordinates under that position?
- What are the responsibilities of that position?
- What are his authorities?
- Interface of this position with other team members?
Team Motivation
Success in an engineering project depends largely on the performance of individual members in the project team. Adequate measures have to be taken to motivate the team members at various levels to achieve the best result. The main motivating factors are Food, Clothing, Shelter, Job Security and Stability, Self-Esteem, Social Recognition, Status, Position, Power etc. Workers' motivation depends on the level in which the worker belongs. The suggested guidelines are:
- Bottom Level Worker - Monetary incentive, Accident coverage etc.
- Middle Level Worker - Service security, Retirement benefit, Appreciation etc.
- Top Level Employee - More power, Promotion, Recognition etc.
Project Plan
This is a document to fully describe the basis for undertaking the project. The document should ensure that the management and the project participants get a clear picture as to where the project is going. The main items to be covered in a typical Project Plan are as follows:
- Project Description and Scope
- Technical Basis - Environmental Impact, Quality, Safety & Health, Approach to Design, Evaluation Studies, Technical Specifications
- Consideration of Cost and Schedule
- Approach to Procurement, Contracting & Construction
- Operation & Maintenance requirements
- Certification requirements
- Project Organization Chart
- Project Procedure requirements
- Computer system and software
- Electronic network for communication & data transmittal
- Clearances from Central/ State Govt. and Local Authorities
- Worksite security/ Watch & Ward
- Applicable Govt. & Local Authority Regulations
- Applicable Owner Standards and Procedures
- Applicable National/ International Standards & Codes
- Claim Settlement and Dispute Resolution Methodology.
Management And Communication Technique
Of the many Project Management Techniques in use Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and Activity Networking Techniques (PERT/CPM) are being used today the world over as these are proven and time tested.
Modern Management Techniques must be used to derive full advantage with computerized analysis, reporting and updating. Effective Communication is of paramount importance with optimum utilization of Internet, E-mail, Computer Networking, Mobile Phones, SMS, Video Conferencing and other state-of-the-art techniques.
10.1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
WBS consists of breaking the project down to manageable Work Packages (WP) with a number of activities under each package and presenting it in a structured manner (Fig. 1, 2). WP is the work required to complete a specific job or process such as a report, design, drawing, procurement, construction, installation etc. WBS groups up the project elements encompassing the total scope of the project. It is a structured representation of the work contents by which the project is divided into progressively smaller elements - the top level representing the entire project and the lowest level the detailed activities. Interrelationship of activities is normally not demonstrated in a WBS. The following benefits are derived from a Project WBS:
- Activity Listing - Easy identification of Work Packages and detailed activities under each package
- Bid Package Listing - Facilitates listing of bids to be prepared and contracts to be awarded
- Responsibility Assignment - Pin-pointing responsibility of each WP to a Project Team Member or to an organizational unit
- Activity Network Preparation - Sequential dependencies of activities can be conveniently ascertained enabling development of the Network of Activities (Fig 3)
- Project Control - Control can be effectively exercised by comparing the actual performance with respect to the plan and applying corrective action.
Activity Network
PERT and CPM are well known techniques and are extensively used in most construction projects. PERT is event oriented (Probabilistic) while CPM is activity oriented (Deterministic). With years of use the techniques have somewhat merged together. What is commonly used today is neither PERT nor CPM but a practical combination of the two and is termed PERT/ CPM. There are two forms of representation ADM - Arrow Diagramming Method and PDM - Precedence Diagramming Method (Fig 4 & 5). While the early planners started with ADM it is not much in use these days. PDM is more commonly used today. Also most Project Management Software Packages are based on PDM based activity networks.
11. Multi - Level Management
In large Industrial and Infrastructure Projects control has to be exercised from different levels of management. Hence, the Management Information System (MIS) has to be compatible with the appropriate level of management. The networks have to be prepared with different degrees of details corresponding to the management level who would be following it up. Networks in three categories as follows are found to be adequate to exercise effective project control.
- CATEGORY I - Master Network encompassing broad activities on the entire project for Top Management follow up.
- CATEGORY II - Zonal Network for specified zones for Middle Management follow up.
- CATEGORY III- Detailed Network for specified work area for day-to-day follow up by the field management.
12. Project Control System
The initial program has to be monitored and updated at regular intervals based on feedback information obtained from various responsibility centers. The updating interval has to be carefully decided depending upon the concerned management level and the degree of control to be exercised on the activities. For most projects monthly updating is commonly adopted. For larger projects bi-monthly or quarterly updating is adopted initially. When a project is found to be slipping and a stricter control has to be exercised, updating at shorter interval has to be adopted.
The results of each updating have to be evaluated with respect to the original plan. If needed the plan has to be modified to get back to the original schedule. This is a continuous process throughout the life of the project. Monitoring and updating is a cycle consisting of the following repetitive operations.
- Original Plan - Schedule for follow-up
- Monitor the plan
- Obtain Feed-back from Responsibility Centers
- Update the Plan & Schedule
- Evaluate the Project Status via-a-vis original plan
- Revise the plan to get back to original schedule
- Repeat the process in each updating.
The progress report indicating the project status should broadly consists of the following components:
- Executive Summary
- Narrative Report
- Quantity, Cost & Schedule
- Program versus Progress
- Advance and Delay, Saving and Overrun
- Problems and Remedial Measures Proposed
- Tables showing quantity and cost status
- Graphs and Visual Progress Charts
- Progress Photographs
- Action Points
13. Management Software
Of the many Project Management Software Packages in use today MICROSOFT (MS) Project and Primavera are globally popular. The software to be used has to be carefully selected keeping in view the following guidelines:
- Specific requirements of the project
- Ease to learn and apply effectively on the project
- Compatibility with the available hardware
- Possibility of upgrading and using on multiple projects
- Cost of the software package.
14. Conclusion
Construction of Industrial and infrastructure Projects in India suffer from large time and cost overruns. Most international experts believe that we are badly deficient in Project Management. Our main shortcomings are on a holistic approach, assigning proper responsibilities, mutual cooperation and understanding, developing a well-knit project team, setting proper priorities, focusing attention on the end objective, overcoming political and legal hurdles, non-availability of site in time and last but not the least arrangement of finance.
Inadequate management strategy is frequently the main cause for failure in an Engineering Project. Fund flow is not the main constraint today. In most developing countries large projects particularly in the Infrastructure and Environment sectors are coming up with internal as well as external funding. In addition to international funding agencies like the World Bank (WB) and Asian Development Bank (ADB), British Funding (DFID), Japanese Banks, American and German Banks, French and Italian institutions are also funding development projects in the third world countries. The major constraints on successful implementation are on effective Engineering Management, Capacity Building and Capacity Utilization.
The Engineering Management in a developing country like India has to rise to the occasion and play it’s part well to ensure successful implementation of the Development Projects.
References
- Basak, S. and Bhattacharya A.K. (2004), "Team Work and Motivation - Essential Requirement for the Success of a Civil Engineering Project" - National Seminar on Role of Management for Infrastructure Development at The Institution of Engineers (India), Kolkata.
- Choudhury, S. (1996), "Project Management" - Tata McGraw Hall Publishing Co. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Kar, D. (2004), "Implementation Strategy - A key to Project Success" - National Seminar on Role of Management for Infrastructure Development at The Institution of Engineers (India), Kolkata.
- Kar, D. (2004), "An Innovative Methodology for Arresting Project Slippage in Water Resources and other Infrastructure Projects" - Ph.D. Registration Report submitted to Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur, Howrah - 711 103.
- Kar, D. (2003), "Successful Implementation of Infrastructure Projects - An Innovative Approach" - National Seminar on Construction Industry for Infrastructure Development organized by American Society of Civil Engineers - India Section at Kolkata.
About the Author (Box Item)
 |
Dr. Amartya Kumar Bhattacharya is Chairman, MultiSpectra Consultants, who holds BCE (Hons.) ( Jadavpur University ), MTech ( Civil ) ( Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ), PhD ( Civil ) ( Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ).
He was a recipient of two medals, four certificates and five books from Don Bosco School, Park Circus, Calcutta. Previously, he was a consulting faculty at Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur and assisted at Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur.
|
Profile of Dr. Amartya Kumar Bhattacharya